What is HOCL?
Hypochlorous Acid
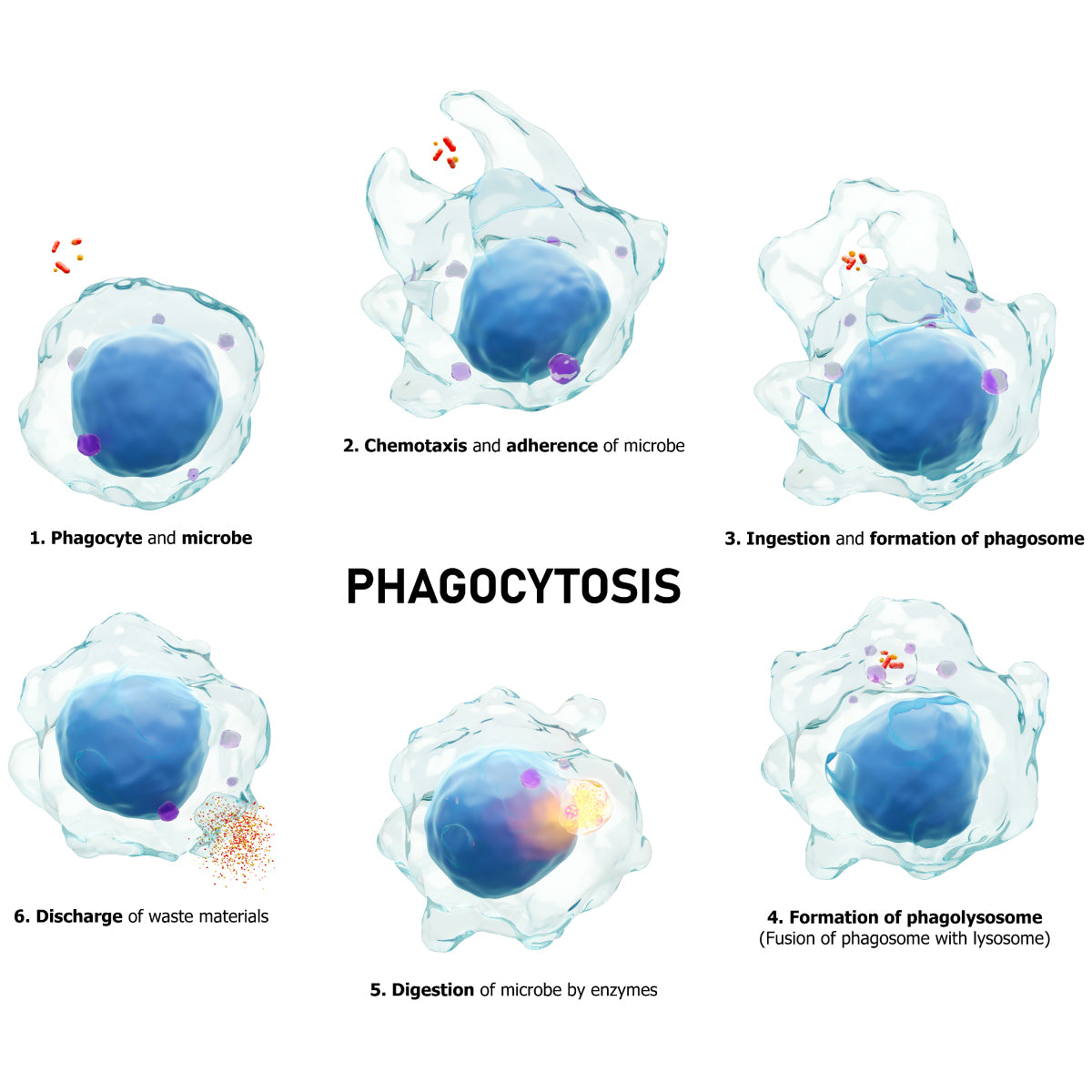
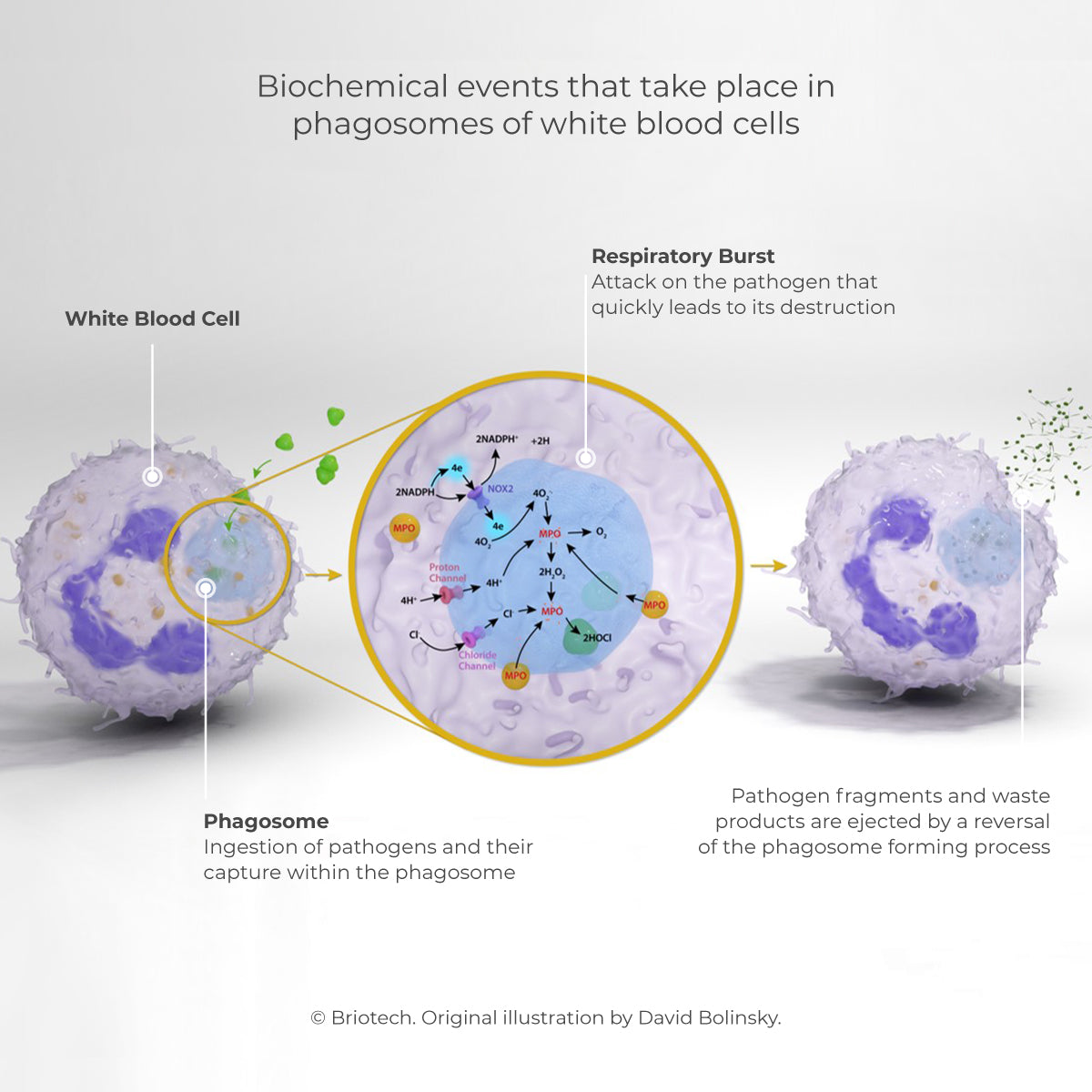
Hypochlorous Acid (HOCl) is a natural part of our internal defense system, produced by white blood cells through a process called phagocytosis. It has been a component of our natural defense system for millions of years. HOCl is the front line of our defense system and serves the dual purpose of fighting all types of germs that try to invade us and triggering a series of biochemical chain reactions to stimulate rapid healing and restore normal structure and function.

How Does Hypochlorous Acid Work?
When produced outside the body, HOCl is an electrolyzed, antimicrobial, biocide solution that inactivates pathogens such as bacteria, viruses, spores, and fungi.
- Works to fight infection, reduce inflammation, and enhance healing
- Part of the healthy response to control injury and recovery
- Consistently shows no adverse effects
- Soothing and fast-acting results
- Will not irritate or aggravate tissue damage at wound sites
- Steady control over the healing process that quickly becomes evident
- No stinging sensation, unlike many other topically applied solutions
- Non-hazardous for use on humans and animals
Real Science in the human body
Harmful pathogens, such as bacteria, spores and viruses, can be found all around us — in the air, on food, plants, animals, and on inanimate surfaces. The human body uses innate, non-specific mechanisms as the first line of defense against pathogens, infection and injury.
The skin itself, and mucous secretions at epithelial membranes, are both important elements of the innate resistance response. But when these are breached, HOCl is immediately generated by the body in response as the key chemical component of innate immunity. A cascade of benefits comes about with this HOCl production.
The mechanism of HOCl production from salt in the body involves intracellular enzymes, but outside the body the process can be mimicked by using controlled application of electrical energy instead — an electrochemical activation (ECA) process.

History of Hypochlorous Acid
As an antimicrobial, antiviral and antifungal that is non-hazardous for all mucosal contact, HOCl hurries healing, works to mitigate scarring, to clear a myriad of skin issues and conditions, can be misted to permeate small crevices for effective odor control and sanitation, and a review of HOCl attributes will show the following citations:
- Reduces skin aging (anti-wrinkle effect) ¹
- Makes blood clot in wounds ²
- Causes fibrinogen oxidation, firmer clots and longer clot lysis period ³
- Stimulates immunity to germs ⁴
- Produces powerful local stimulants of wound healing/germ killing ⁴
- Makes new skin cells grow over wounds and reorganizes scar fibers ⁵
- Leads to long lasting local effects in the body ⁵
While the 100 year history of Hypochlorous Acid has provided indisputable evidence of its efficacy in healing and use in disinfection, and over 500 peer-reviewed, published papers universally document significant beneficial results, the widespread use of HOCl has remained fairly stagnant, and the primary limiting factor to broad adoption of this important technology, historically, has been due to its lack of stability.

HISTORY OF HYPOCHLOROUS
